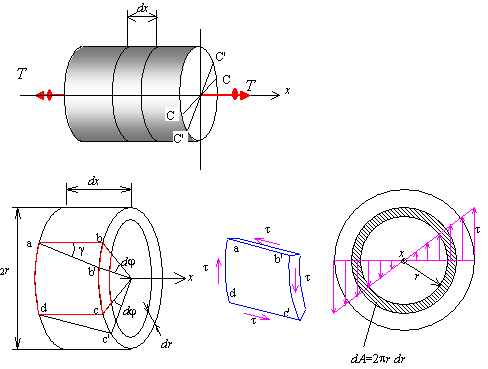
\[
\tau=G\gamma
\\
\gamma=\dfrac{\stackrel{\huge\frown}{CC'}}{dx}=r\dfrac{d\phi}{dx}
\]
一様な断面を持つ軸では全長を\(l\)、ねじれ角\(\phi\)を用いて
\[
\dfrac{d\phi}{dx}=\dfrac{\phi}{l}
\\
\tau=G\dfrac{r\phi}{l}
\]
仮想断面での中心軸周りのトルクは
\[
T=\int dT=\int r\tau dA=\int rG\dfrac{r\phi}{l}dA=G\dfrac{\phi}{l}\int r^2dA
\]
ここで\(\int r^2dA\)を\(I_{p}\)(断面二次極モーメント)とすると
\[
T=G\dfrac{\phi}{l}I_{p}=\dfrac{\tau}{r}I_{p}
\]
式変形して
\[
\tau=\dfrac{T}{I_{p}/r}
\]
このとき、仮想断面での最大応力\(\tau_{max}\)は\(r\)が最大のとき(\(r_{max})\)となり
\[
\tau_{max}=\dfrac{T}{I_{p}/r_{max}}
\]
このとき
\( \dfrac{I_{p}}{r_{max}} \)を\(Z_{p}\)(極断面係数)とすると
\[
\tau_{max}=\dfrac{I_{p}}{Z_{p}}
\]
 \[
\tau=G\gamma
\\
\gamma=\dfrac{\stackrel{\huge\frown}{CC'}}{dx}=r\dfrac{d\phi}{dx}
\]
一様な断面を持つ軸では全長を\(l\)、ねじれ角\(\phi\)を用いて
\[
\dfrac{d\phi}{dx}=\dfrac{\phi}{l}
\\
\tau=G\dfrac{r\phi}{l}
\]
仮想断面での中心軸周りのトルクは
\[
T=\int dT=\int r\tau dA=\int rG\dfrac{r\phi}{l}dA=G\dfrac{\phi}{l}\int r^2dA
\]
ここで\(\int r^2dA\)を\(I_{p}\)(断面二次極モーメント)とすると
\[
T=G\dfrac{\phi}{l}I_{p}=\dfrac{\tau}{r}I_{p}
\]
式変形して
\[
\tau=\dfrac{T}{I_{p}/r}
\]
このとき、仮想断面での最大応力\(\tau_{max}\)は\(r\)が最大のとき(\(r_{max})\)となり
\[
\tau_{max}=\dfrac{T}{I_{p}/r_{max}}
\]
このとき
\( \dfrac{I_{p}}{r_{max}} \)を\(Z_{p}\)(極断面係数)とすると
\[
\tau_{max}=\dfrac{I_{p}}{Z_{p}}
\]
\[
\tau=G\gamma
\\
\gamma=\dfrac{\stackrel{\huge\frown}{CC'}}{dx}=r\dfrac{d\phi}{dx}
\]
一様な断面を持つ軸では全長を\(l\)、ねじれ角\(\phi\)を用いて
\[
\dfrac{d\phi}{dx}=\dfrac{\phi}{l}
\\
\tau=G\dfrac{r\phi}{l}
\]
仮想断面での中心軸周りのトルクは
\[
T=\int dT=\int r\tau dA=\int rG\dfrac{r\phi}{l}dA=G\dfrac{\phi}{l}\int r^2dA
\]
ここで\(\int r^2dA\)を\(I_{p}\)(断面二次極モーメント)とすると
\[
T=G\dfrac{\phi}{l}I_{p}=\dfrac{\tau}{r}I_{p}
\]
式変形して
\[
\tau=\dfrac{T}{I_{p}/r}
\]
このとき、仮想断面での最大応力\(\tau_{max}\)は\(r\)が最大のとき(\(r_{max})\)となり
\[
\tau_{max}=\dfrac{T}{I_{p}/r_{max}}
\]
このとき
\( \dfrac{I_{p}}{r_{max}} \)を\(Z_{p}\)(極断面係数)とすると
\[
\tau_{max}=\dfrac{I_{p}}{Z_{p}}
\]